analysis projects & research.
selection of applied economic analyses using econometric and statistical modeling.
✧ Opioid Epidemic Economic Impact Study ✧ full paper here ✧
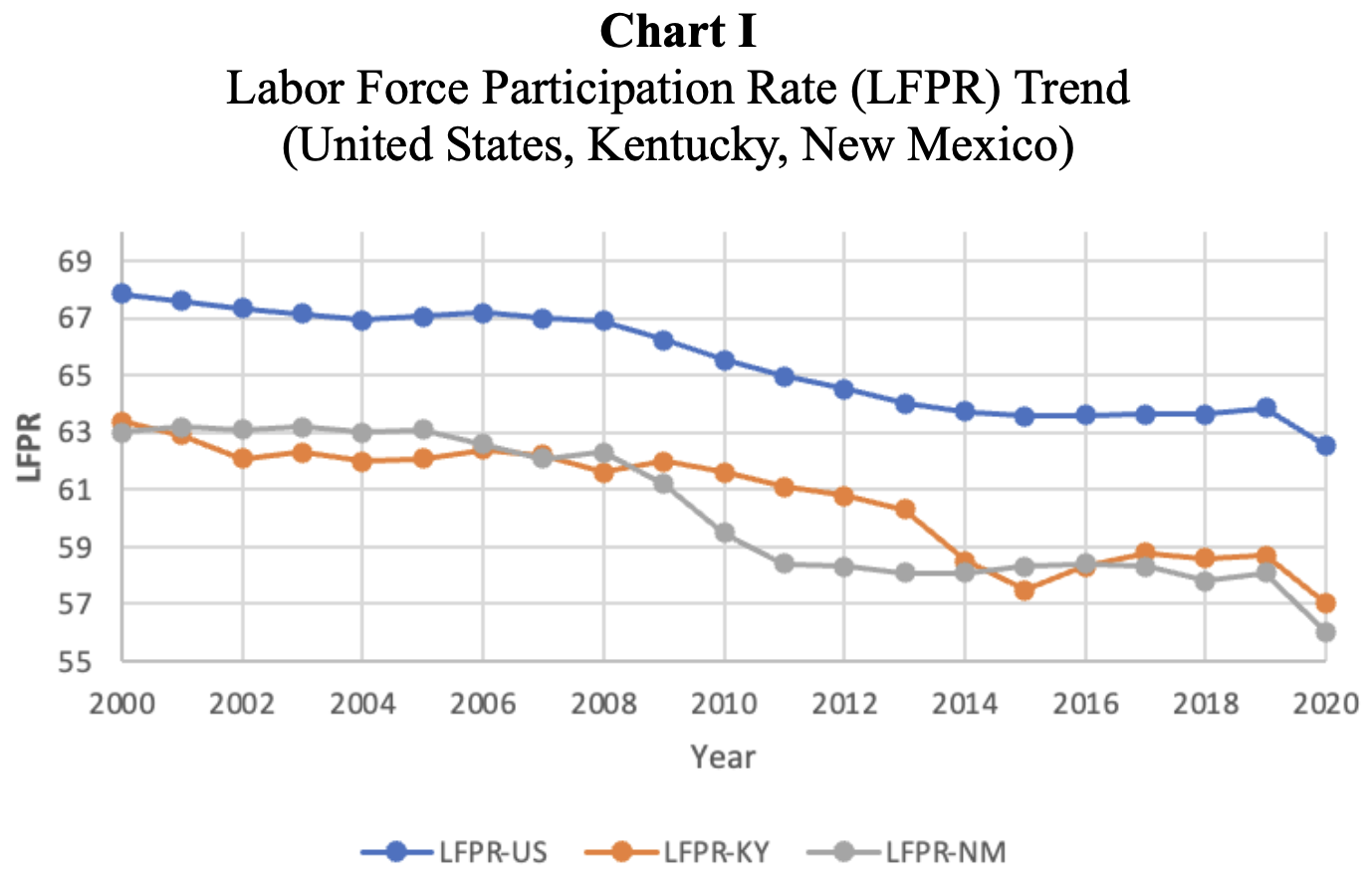
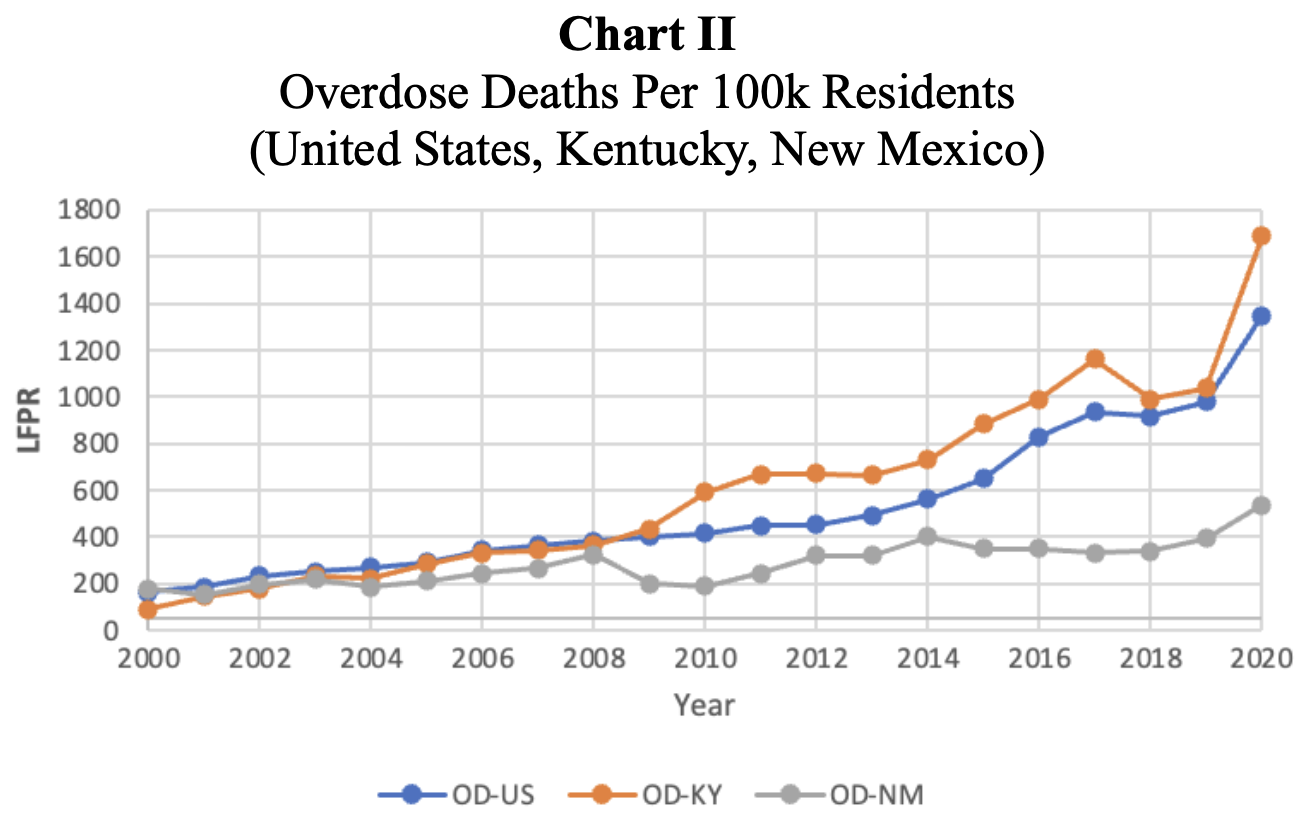
overview ✧This project investigated the socioeconomic and labor market effects of the U.S. opioid epidemic, focusing on how rising misuse rates influence employment, healthcare expenditure, and productivity. Drawing from national datasets including BEA, BLS, CDC, CMS, KFF, and the U.S. Census Bureau, the analysis quantified both direct and indirect economic costs across state economies.
data & methods ✧Built a comprehensive panel dataset and applied pooled OLS and fixed-effects regression models in Stata, supported by time-series trend analysis to capture long-term effects. Conducted data cleaning, normalization, and variance decomposition to manage cross-state disparities and regional policy differences.
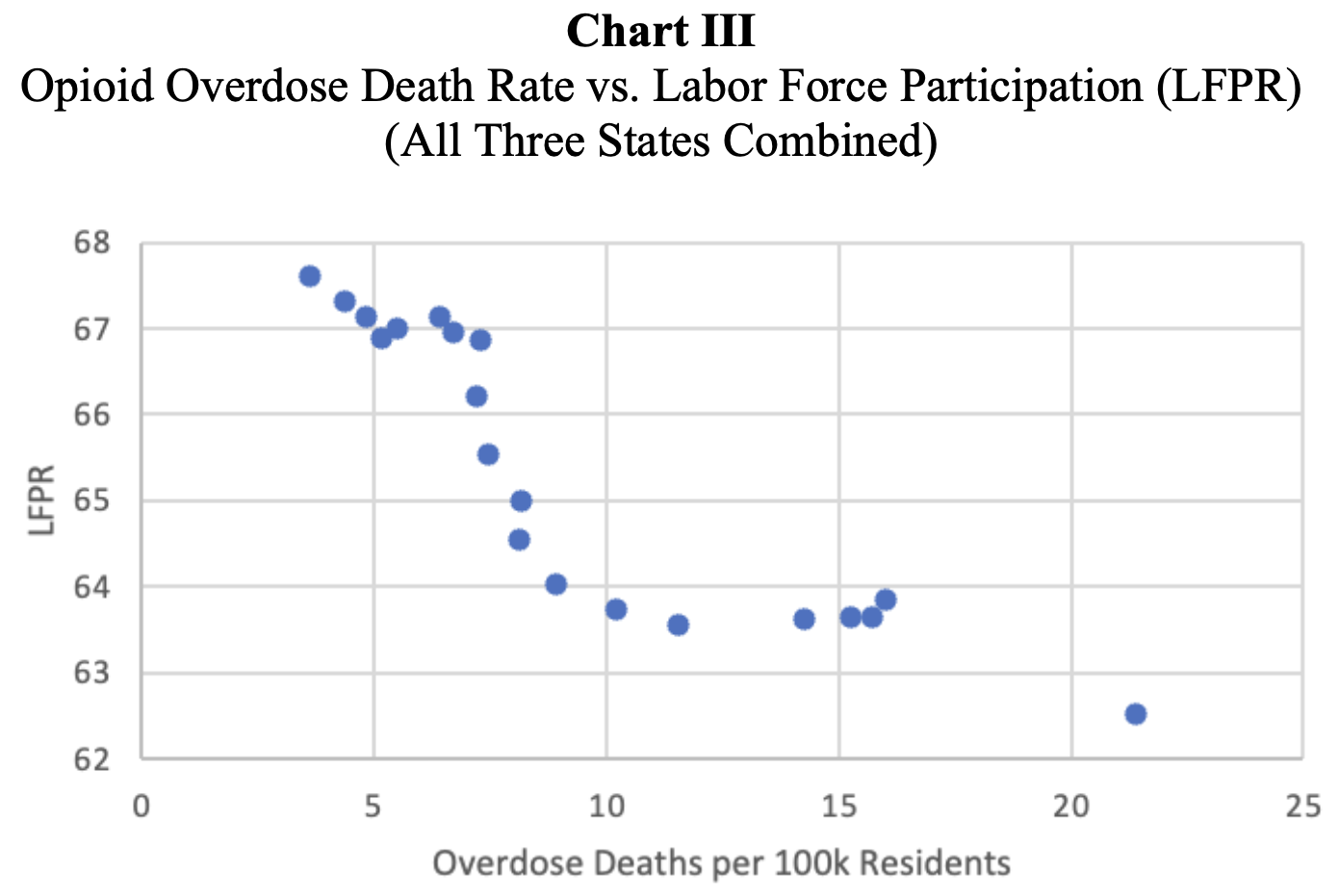
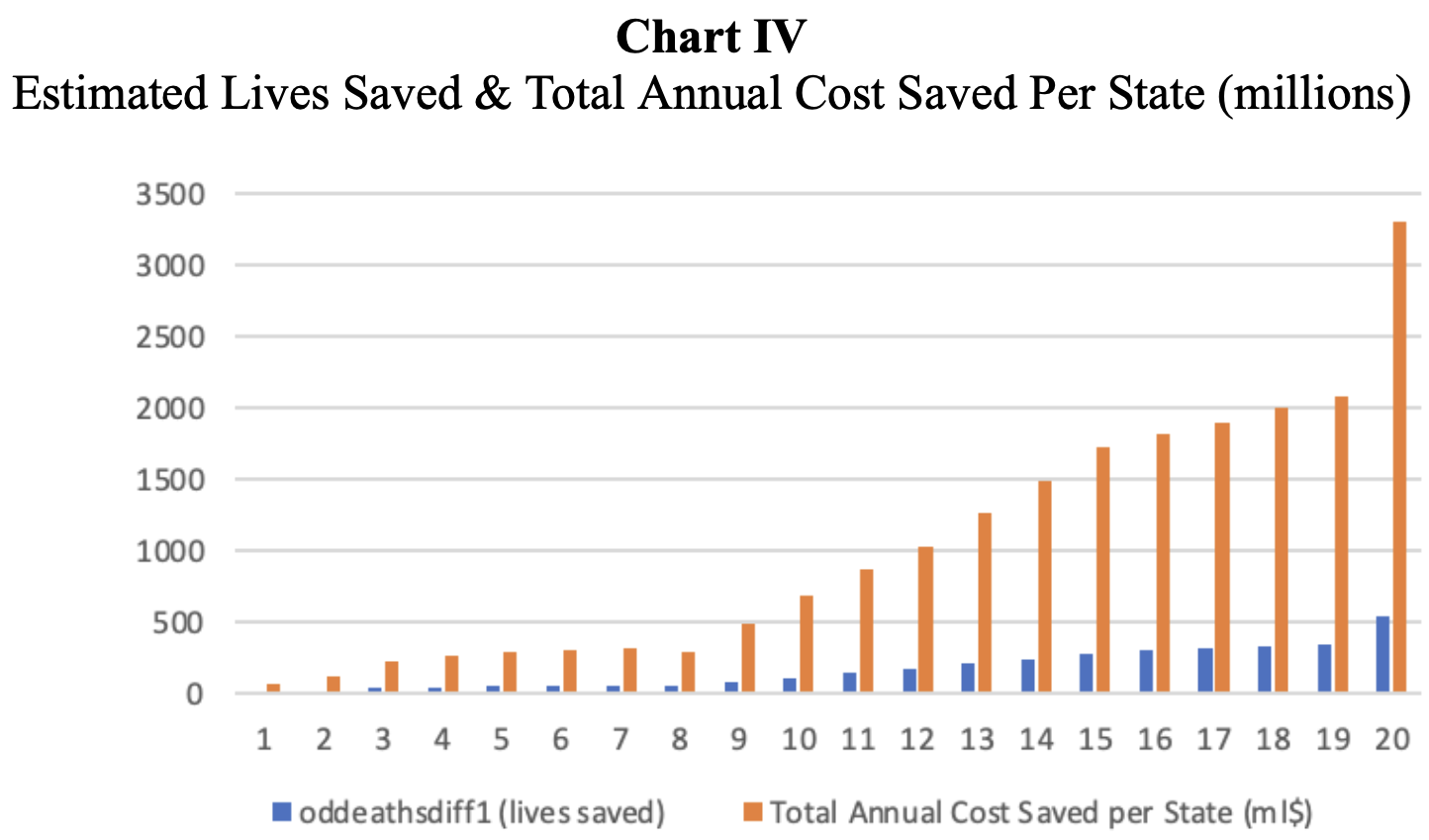
key insights ✧Findings revealed a strong negative correlation between opioid prevalence and labor participation, with states experiencing higher dependency showing 15–25% greater healthcare expenditures relative to GDP. Economic losses were especially concentrated in rural and low-income regions.
implications ✧Results demonstrate that the opioid crisis imposes a significant macroeconomic drag, emphasizing the need for data-informed policy that aligns healthcare initiatives with labor force rehabilitation and regional development planning.
✧ Smart Growth & Urban Development Evaluation ✧ full paper here ✧
overview ✧This research assessed the impact of Smart Growth policies on sustainable urban development, infrastructure efficiency, and investment outcomes. The goal was to evaluate whether data-driven policy adoption translated to more equitable and efficient growth patterns.
data & methods ✧Utilized panel regression analysis and Three-Stage Least Squares (3SLS) estimation in Stata to address endogeneity between infrastructure spending and urban density. Compiled multi-year datasets integrating city-level investment, zoning, and population growth indicators. Excel dashboards were used to visualize trends, regressions, and performance metrics.
key insights ✧Results indicated that Smart Growth adoption correlated with improved infrastructure efficiency and moderated housing density expansion. Cities with stronger policy implementation showed measurable gains in resource allocation and reduced sprawl intensity.
implications ✧The study supports Smart Growth as an effective framework for sustainable urban planning. It highlights the value of econometric evaluation and spatial data integration in shaping future development and infrastructure investment strategies.
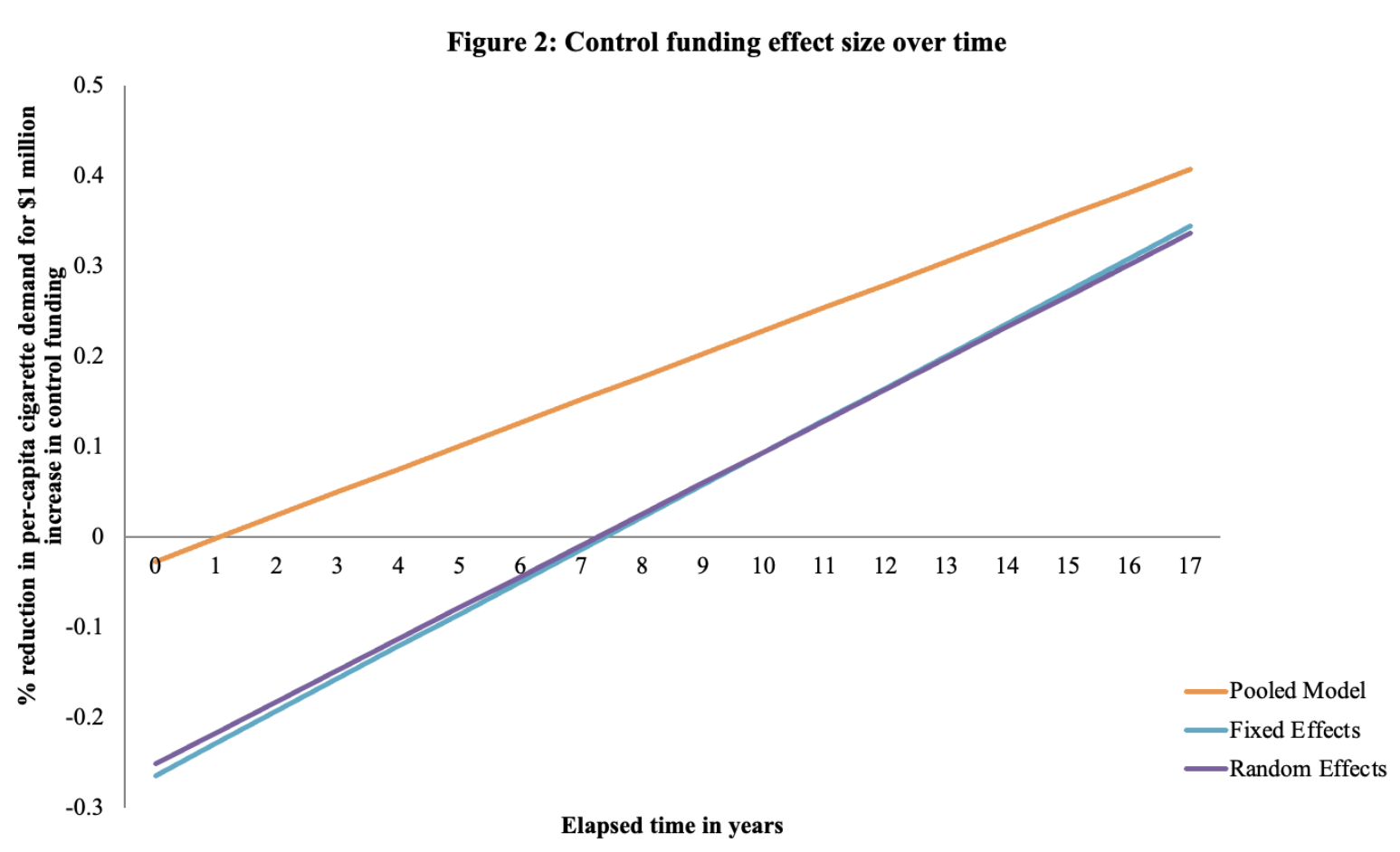
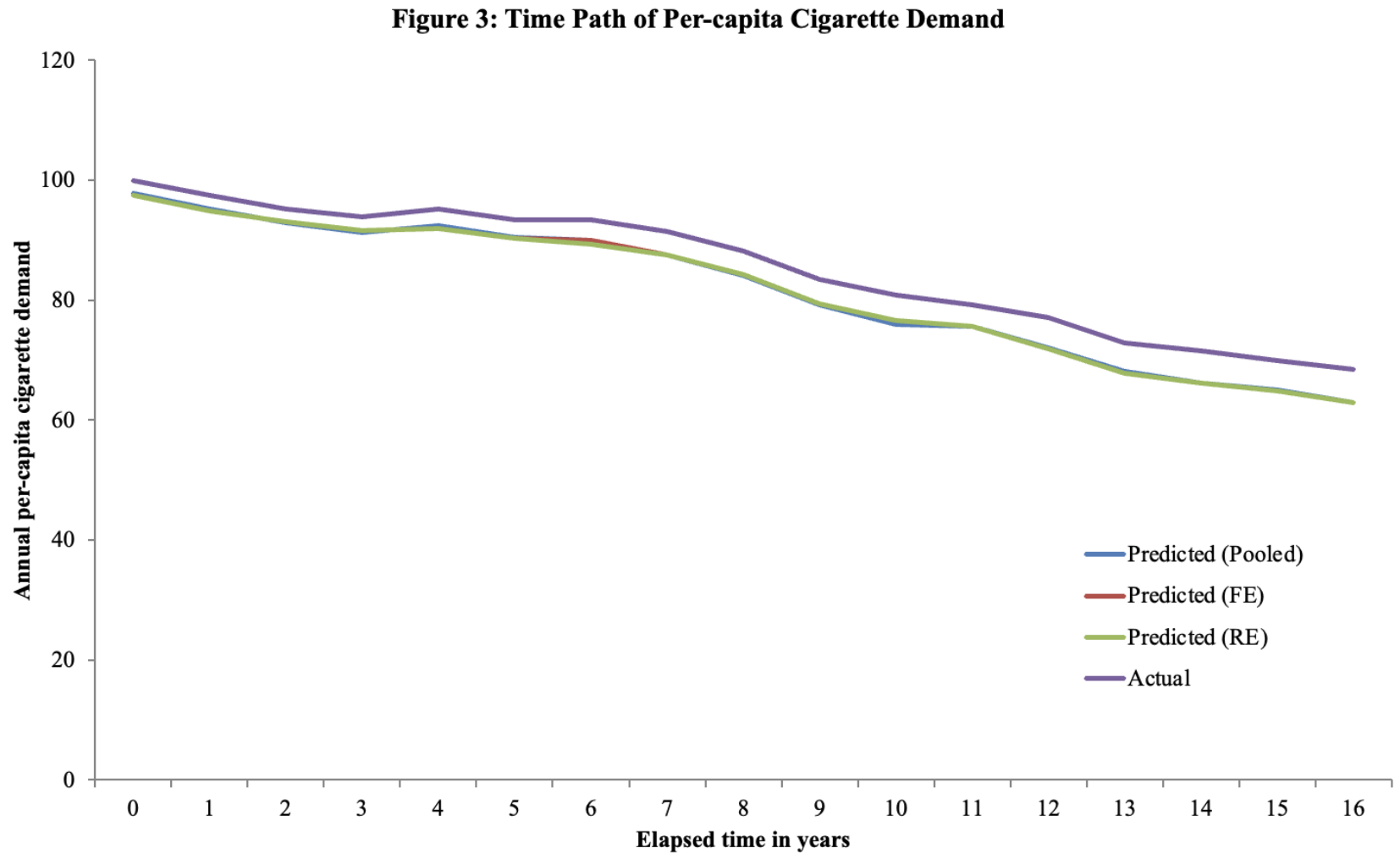
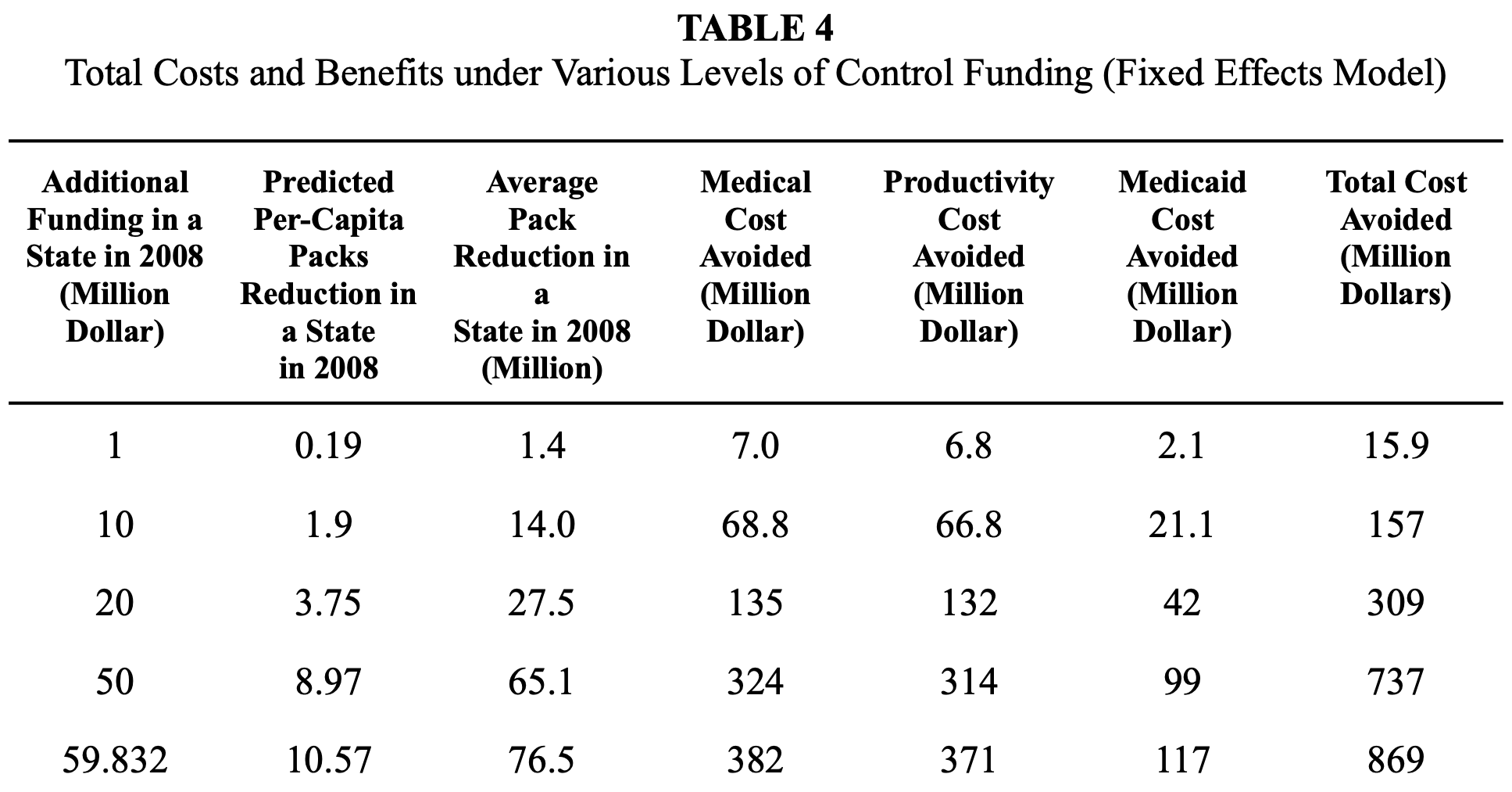
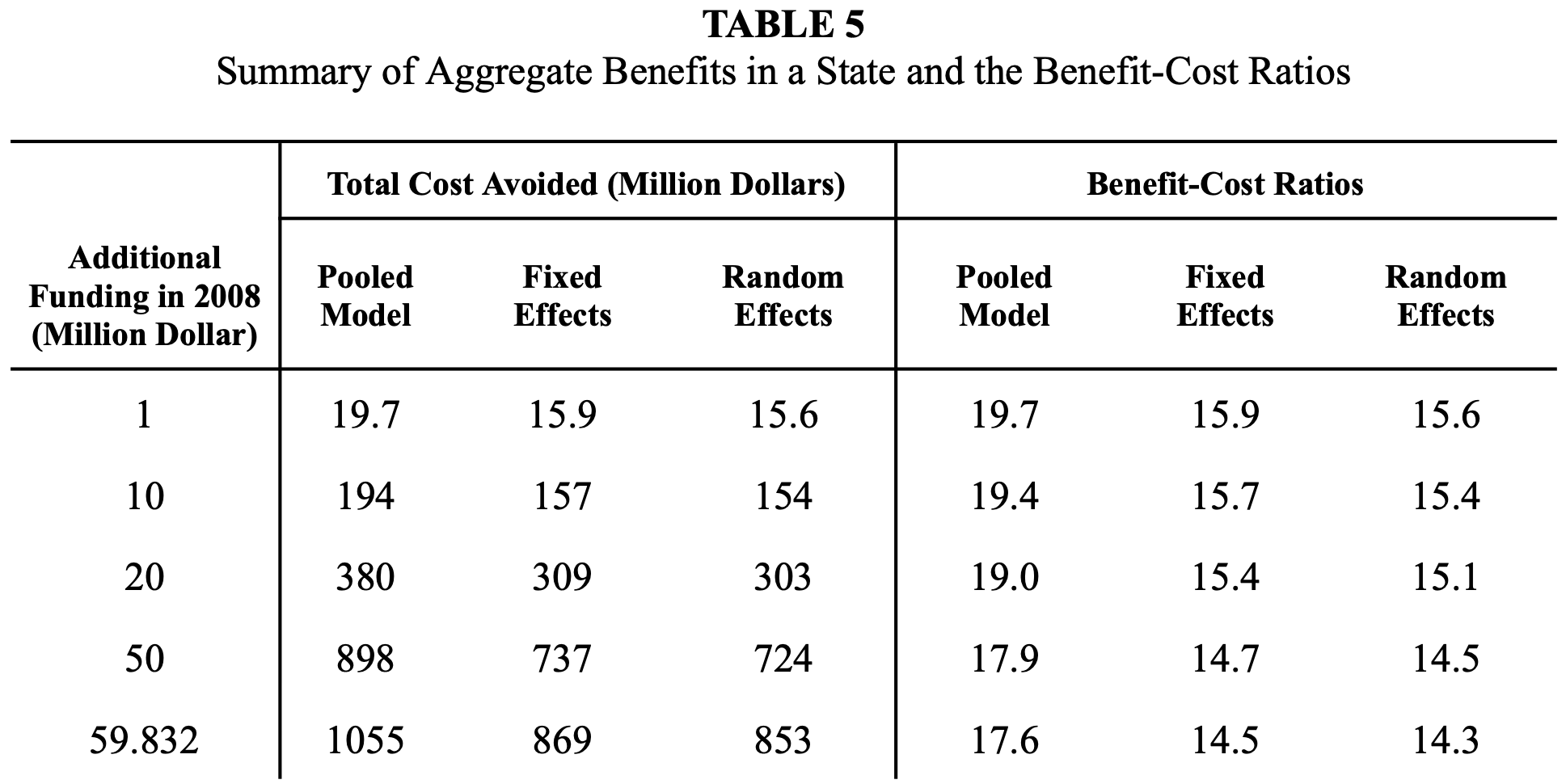
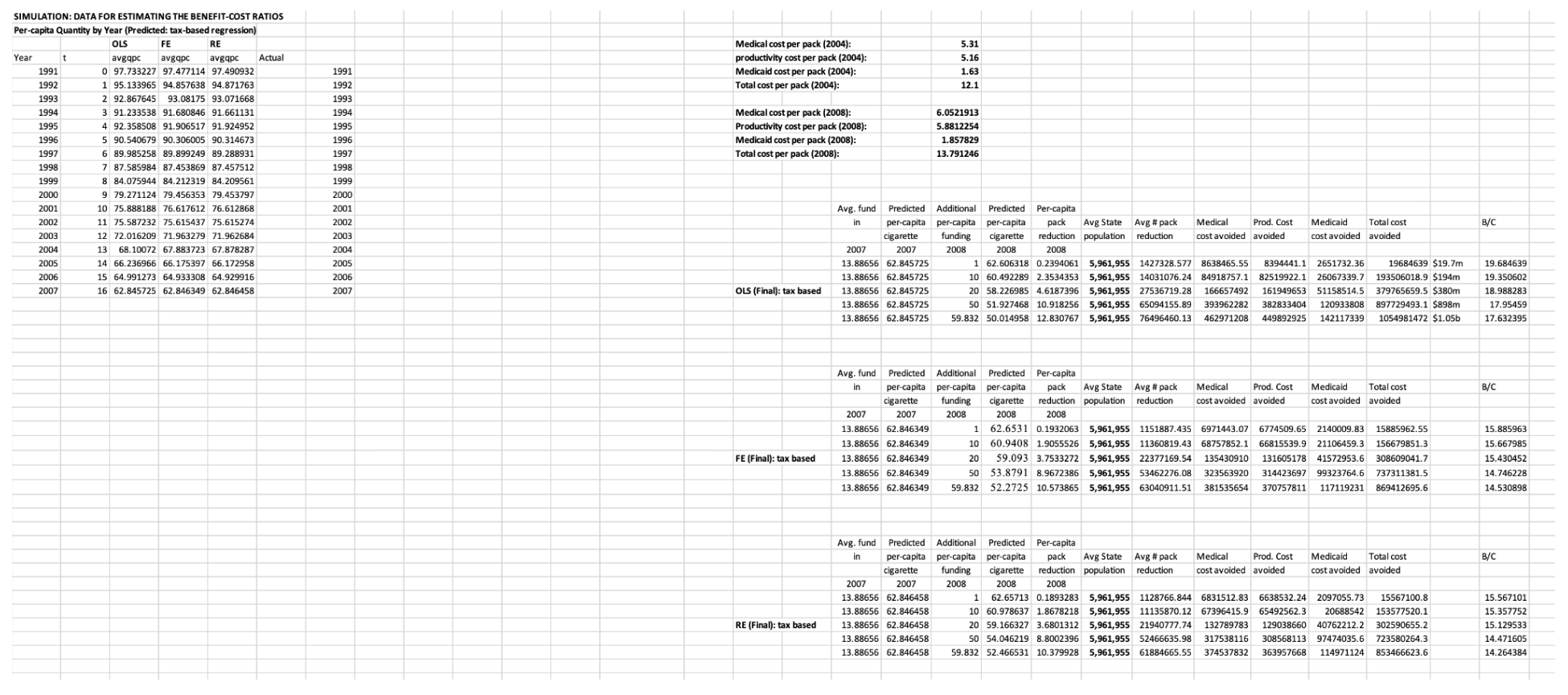
✧ Tobacco Consumption & Tax Elasticity Analysis ✧ full paper here ✧
overview ✧This project examined how variations in state-level cigarette taxation affect consumption patterns and price elasticity across the United States. The study aimed to quantify behavioral responses to taxation and provide evidence for public health and fiscal policy design.
data & methods ✧Conducted cross-sectional and time-series regression analyses in Stata and Excel, incorporating price indices, demographic controls, and regional dummy variables. Performed data preprocessing, correlation testing, and sensitivity analysis to ensure model robustness.
key insights ✧Results showed a significant negative elasticity between tax rates and per capita tobacco consumption, with stronger responses in states with historically higher baseline usage. Elasticity estimates confirmed that even moderate tax increases lead to meaningful declines in sales volume.
implications ✧The findings affirm the effectiveness of excise taxes as a tool for reducing tobacco use and improving public health. They also underscore the importance of data-driven fiscal policy in shaping long-term behavioral outcomes.
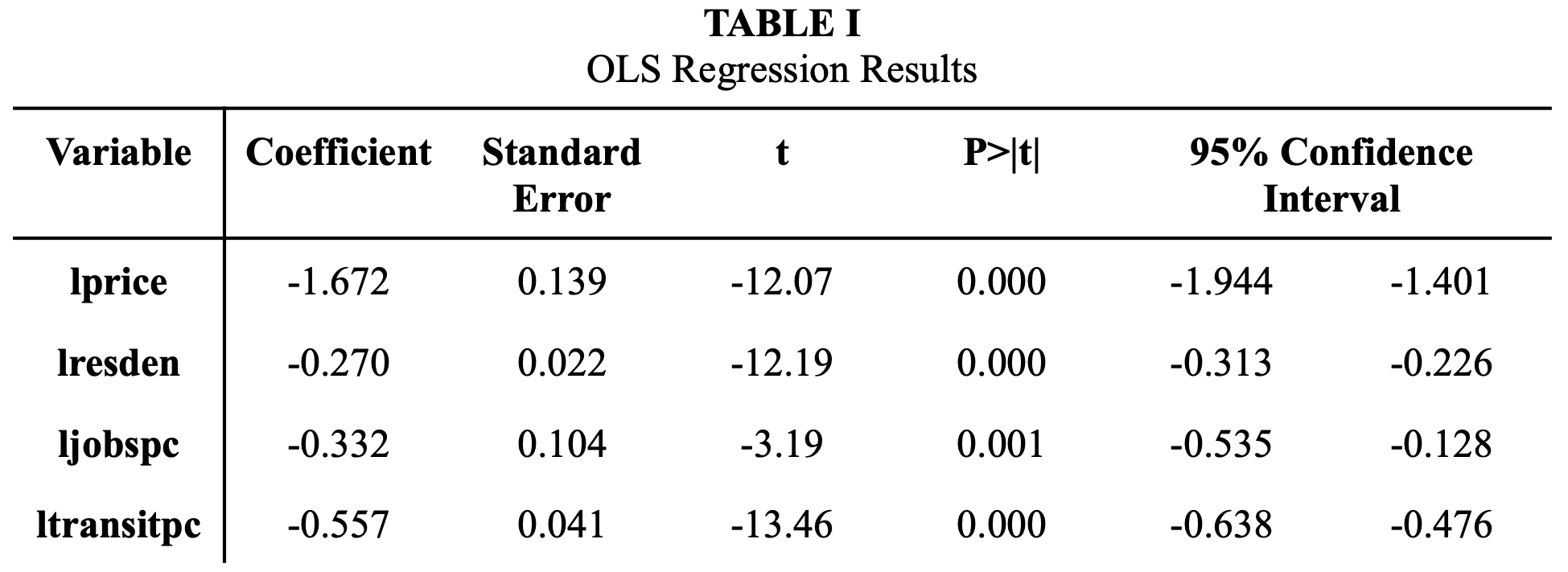
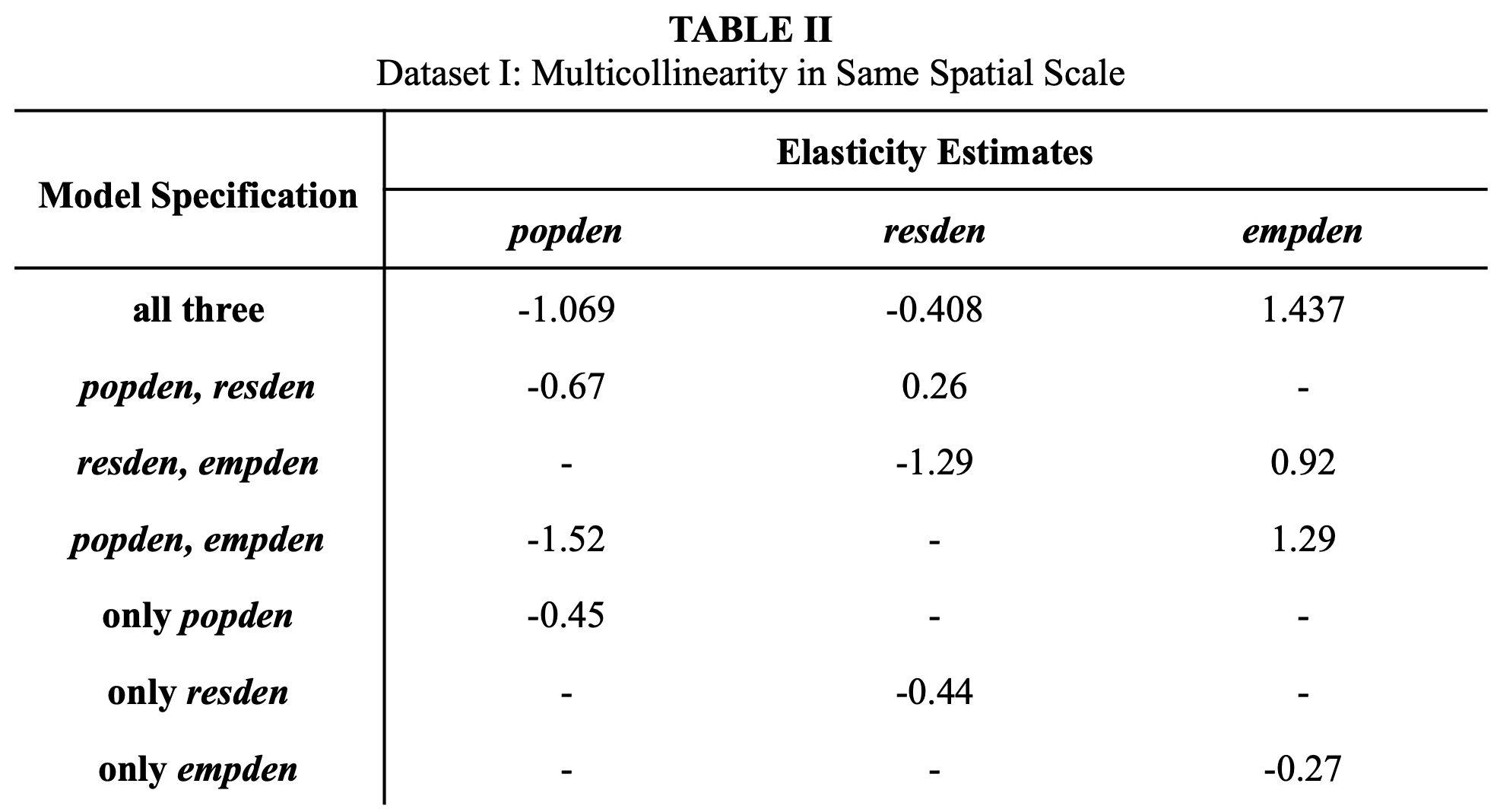
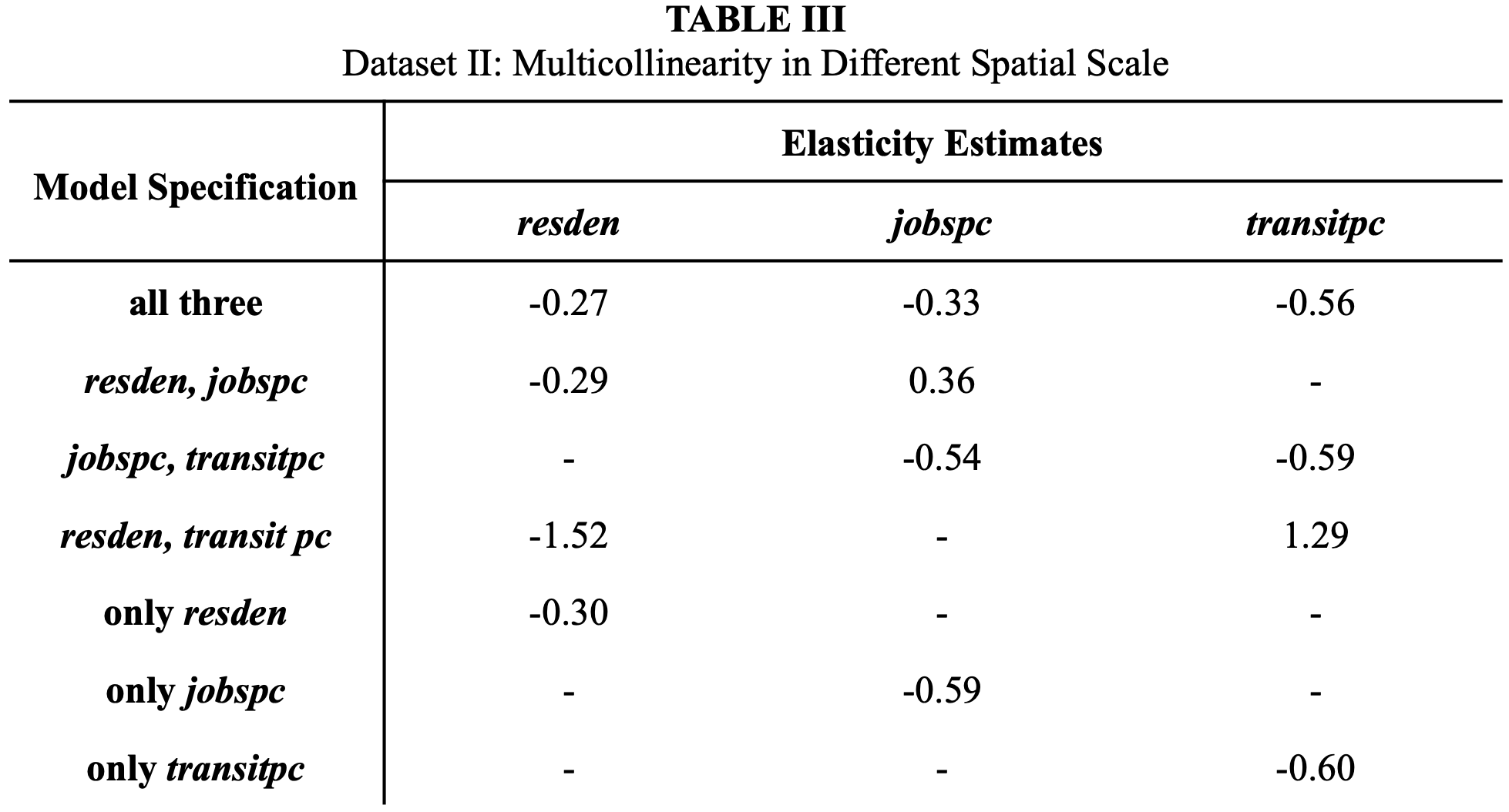
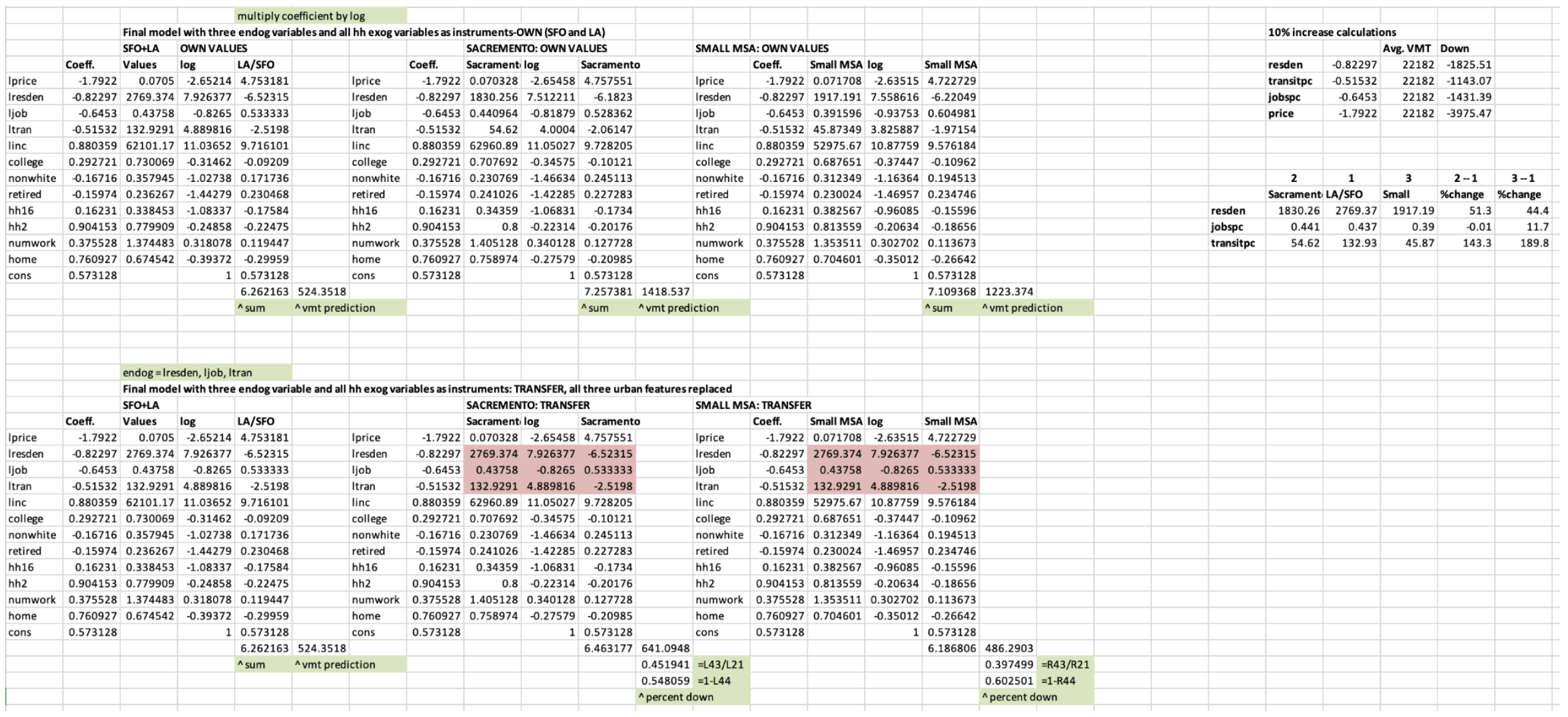
✧ Housing Market Dynamics & Price Volatility Analysis ✧ full paper here ✧
overview ✧This research explored the determinants of housing market volatility and affordability across major metropolitan regions, focusing on the interplay between supply constraints, interest rate shifts, and income growth.
data & methods ✧Built econometric models using OLS and time-series regression techniques in Stata to estimate relationships between key variables. Employed Excel for trend visualization, variance analysis, and forecast modeling. Conducted data cleaning and transformation using multi-year housing, mortgage, and economic datasets.
key insights ✧Results indicated that interest rate fluctuations and limited housing supply were the strongest predictors of short-term price volatility. Income growth showed a lagged but significant impact on long-run affordability.
implications ✧The analysis underscores how monetary and housing policies interact to shape price stability. Findings advocate for policy mechanisms that expand supply elasticity and improve lending transparency to stabilize housing markets and enhance affordability.